3GPP stands for 3rd Generation Partnership Project, which is a global initiative, producing specifications and studies for mobile systems.
3GPP was created in 1998 to develop 3rd generation mobile standards, based on a widely adopted mobile system called GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications).
3GPP constitutes Organizational Partners and Market Representation Partners.
An Organizational Partner is any open standardization organization, which has a national, regional or other officially recognized status and the capability and authority to define, publish and set standards within 3GPP scope, in that nation or region.
Currently, there are 7 such organizational partners.
Market representation partners are any organization which has been invited by these 7 Organizational Partners to take part in 3GPP, which has the ability to offer an advice to 3GPP and to bring a consensus view of market requirements.
Watch ‘Introduction to 3GPP’ on YouTube: ![]() https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L9rS2DS6ZOU
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L9rS2DS6ZOU
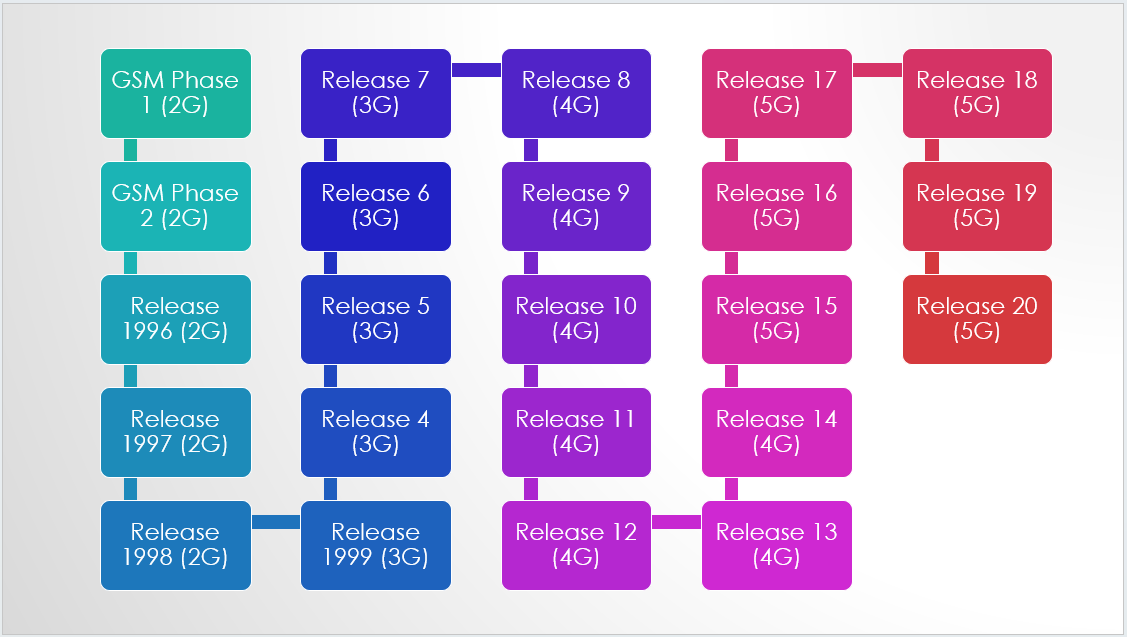
3GPP releases are the stepping stones to introduce new features and functionality to meet constantly changing market requirements.
Each release contains a set of technical reports and technical specifications with which a complete mobile system can be constructed to offer much needed services.
3GPP uses a system of parallel ‘releases’ which provide developers with a stable platform for the implementation of features at a given point and then allow for the addition of new functionality in subsequent releases.
A release differs from previous release by having added functionality.
Generally, 3GPP releases new features around every 12-18 months.
Watch ‘Introduction to 3GPP Releases’ Video on YouTube: ![]() https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AD5gfKAiJ4M
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AD5gfKAiJ4M
3GPP specifications are made available free of charge.
The term ‘3GPP Specification’ covers
GSM specifications including GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) and EDGE (Evolved Data rates for GSM Evolution), UMTS specifications including HSPA (High Speed Packet Access), LTE specifications including LTE Advanced and LTE Advanced Pro, 5G specifications including 5G Advanced and 6G specifications.
3gpp specifications are documented at various stages which includes,
Stage 0 refers to these technical reports which are produced based on feasibility study.
Stage 1 – these specifications refer to the overall service description from the service subscribers and users’ point of view. In these stage 1 specifications, network is seen as a single entity which provides services to the user.
Stage 2 – these specifications describe the overall organization of the network functions to map service requirements into network capabilities.
Stage 3 – these are the specifications which provide the concrete implementation of the functionality and of the protocols. These specifications define switching and signalling capabilities, needed to support the services defined in Stage 1.
Stage 4 – these are the test specifications to confirm the functionality.
Watch ‘Introduction to 3GPP Specifications’ Video on YouTube: ![]() https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WDPLvBUMzpM
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WDPLvBUMzpM
From the time 3rd Generation Partnership Project formed in 1998, to build a 3rd Generation Mobile System, based on well adopted one of the 2nd Generation Mobile System i.e., GSM (Global System for Mobile communications), 3GPP has been producing the standards for multiple variants of mobile systems, which are driving the world of mobile communications over the decades.
It is important to understand, the impact of these 3GPP technologies that are creating to the society as a whole.
As per ‘The Mobile Economy 2024’ report published by GSMA (GSM Association), there are around 5.6 billion people that are subscribed to a mobile service by 2023, i.e., 69% of the global population.
The report also stated that the impact of mobile connectivity is evidenced by its contribution to the global economy.
In 2023, mobile technologies and services generated 5.4% of global GDP (Gross Domestic Product), a contribution that is amounted to 5.7 trillion dollars of economic value.
Report also mentioned that the mobile industry supported around 35 million jobs.
Watch ‘Introduction to 3GPP Technologies’ Video on YouTube: ![]() https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YkkRxSwvHc8
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YkkRxSwvHc8
Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) is considered as 2nd Generation of Mobile System, designed to offer both voice and non-voice services and facilities, that are compatible with already existing fixed networks such as Public Switched Telephone Networks (PSTN), Integrated Services Digital Networks (ISDN) through the standardized access to these networks.
GSM to provide certain services and facilities that are exclusive to mobile stations, which are not feasible in the case of fixed networks.
GSM network should facilitate automatic roaming, locating, and updating mobile subscribers.
GSM network should provide subscribers a service with a good quality level, matching to fixed networks.
GSM network should provide services to a wide range of mobile stations, including vehicle mounted stations, portable stations and handheld devices.
Watch ‘Introduction to GSM (Global System for Mobile communications’ Video on YouTube: ![]() https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tCqtleSCw_o
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tCqtleSCw_o
Let us continue our discussion on one other 3GPP Technology i.e., UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System), which is considered as 3rd Generation Mobile Technology of 3GPP variant.
UMTS Objectives are aligned with the requirements set up by ITU (International Telecommunications Union) as part of IMT-2000.
UMTS to offer High bit rate services, UMTS to provide high bit rate services up to initially 2 Mbit/s.
Security, ensuring that information generated by or relating to a UMTS user or subscriber, is adequately protected against misuse or misappropriation. It is also necessary to ensure that the resources and services provided by a UMTS service provider or network operator are adequately protected against misuse or misappropriation.
Migration and evolution, to allow a cost-effective introduction of UMTS, a migration path to exist, whereby portions of existing systems and networks may be exploited for the implementation of UMTS. Furthermore, UMTS shall allow the easy introduction of technology advancements and service applications without undue impact on existing users and terminal equipment.
When it comes to telecommunications services offered by UMTS, all the services that are available in GSM i.e., Basic telecommunication services including bearer and tele services along with supplementary services and network features are supported in UMTS. In addition to these services, UMTS offers additional features.
Watch ‘Introduction to UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System’ Video on YouTube: ![]() https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e1TFho49F3s
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=e1TFho49F3s
LTE (Long Term Evolution), which is considered as 4th Generation Mobile Technology of 3GPP variant.
LTE is an evolution from the previous generation of technology i.e., UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System), which is considered as a 3rd Generation Mobile System of 3GPP variant.
Short to medium term evolution include, optimization of radio access network architecture, especially for packet data communication to improve the efficiency of the network and to lower the implementation costs, harmonized IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS), to provide the opportunity of service transparency, seamless roaming and common applications across all evolving IMT-2000 systems, packet data communication optimization in the core and radio access network architectures to improve the efficiency of the network.
When it comes to, Long Term Evolution objectives, which are driven by market trends, understanding of user requirements and the availability of new network and wireless access technologies. Including, Radio access performance improvements, across spectral efficiency, higher bit rates and shorter delays.
Spectral efficiency targets include 5 to 10 bits per second per hertz in an isolated cell, while 2 to 3 bits per second per hertz in a multi-cellular environment. Peak data rate targets include up to 100 Mega bits per second in full mobility, wide area deployments, while up to 1 Giga bits per second in low mobility, local area deployments.
Watch 'Introduction to LTE (Long Term Evolution)" Video on YouTube: ![]() https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l5T6nwBr1Qo
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=l5T6nwBr1Qo
5G, which is considered as 5th Generation Mobile System of 3GPP variant.
Key contributions of 5G mobile communications include,
Wireless infrastructure to connect the world, due to unprecedented adoption of mobile devices, the importance of mobile connectivity is becoming similar to that of access to electricity. Broadband connectivity acts as one of the key pillars to enable mobile service delivery and information exchanges.
New ICT Market, Integrated Information and Communication Technology to drive economies around the globe. As an example, the accumulation, aggregation, and analysis of big data to deliver customized networking services for enterprises and social network groups in wireless networks.
Bridging the digital divide, 5G to help closing the gaps caused by an increasing Digital Divide. Affordable, sustainable and easy-to-deploy mobile and wireless communication systems, while effectively saving energy and maximizing efficiency.
New ways of communication, 5G to enable sharing of any type of contents anytime, anywhere through any device.
New forms of education, 5G to change the method of education by providing easy access to digital textbooks or cloud-based storage of knowledge on the internet, boosting applications such as e-learning, e-health, and e-commerce.
Promote energy efficiency, 5G enables energy efficiency across a range of sectors of the economy, by supporting machine to machine communication and solutions such as smart grid, teleconferencing, smart logistics and transportation.
Social changes, 5G networks make it easier to quickly form and share public opinions. Opinion formation of a huge number of connected people due to their ability to exchange information anytime anywhere will become a key driver of social changes.
New art and culture, enable people to create works of art or participate in group performances or activities, such as a virtual chorus, flash mob, co-authoring or song writing. People connected to a virtual world are able to form new types of communities and establish their own cultures.
Watch ‘Introduction to 5G (5th Generation Mobile System)’ Video on YouTube: ![]() https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R8NOMz3O93k
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R8NOMz3O93k
IMS has been the choice of network implementation, regardless of the underlying supported mobile systems i.e., UMTS, LTE and 5G, to offer basic telecommunication services such as voice and messaging and supplementary services over the IP based protocols.
The IP Multimedia System (IMS) is a standardized architectural framework developed by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project, popularly known as 3GPP, for delivering IP-based multimedia services.
IMS supports the convergence of voice, video, messaging, and data services over both fixed and mobile networks, enabling seamless communication and enhanced user experiences.
IMS leverages the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) for session control, allowing the setup, management, and termination of multimedia sessions.
IMS architecture is designed to be scalable, flexible, and interoperable, ensuring that it can support a wide range of services and adapt to the evolving needs of the telecommunications industry.
By providing a standardized and modular approach, IMS facilitates the introduction of new services, improves quality of service (QoS), and enhances the overall reliability and efficiency of the network.
IMS is a critical component for operators looking to deliver high-quality, next-generation multimedia services to their subscribers.
Watch ‘IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS)’ Video on YouTube: ![]() https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KiYL06HEb5s
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KiYL06HEb5s
6th Generation Mobile System i.e., 6G, which is the next generation of wireless communication technology, expected to be available around year ‘2030’. 3GPP introduced a new logo in its preparations for this next generation of mobile system.
Key objectives of this future generation mobile technology include
Inclusivity, 6G to bridge the digital divide by ensuring that people in rural and low-income regions have access to high-speed internet and advanced communication services.
Ubiquitous connectivity, 6G promises to transform the way we live, work, and interact with the world. By providing seamless, high-speed, and reliable communication everywhere, 6G will enable new applications and opportunities, driving technological innovation and societal progress.
Sustainability, 6G technology has the potential to significantly contribute to sustainability by enhancing energy efficiency, supporting smart cities and agriculture, improving climate monitoring, and promoting digital inclusion.
Innovation, 6G technology promises to be a catalyst for innovation, driving advancements in communication, automation, and connectivity. By enabling new applications and enhancing existing ones, 6G will transform industries, improve quality of life, and pave the way for a more connected and intelligent future.
Enhanced security and resilience, 6G technology promises to bring unprecedented advancements in connectivity, but it also requires robust security and resilience measures to address emerging threats. By integrating advanced encryption, AI-driven security, and resilient network designs, 6G will provide a secure and reliable foundation for the future of communication.
Standardization and interoperability, these are crucial for the successful deployment of 6G technology. Ensuring that different systems and devices can work together seamlessly is essential for creating a cohesive and efficient global network.
Interworking, it is a key component of 6G technology, ensuring seamless connectivity and supporting a wide range of applications and services. By integrating different network systems and technologies, 6G can provide ubiquitous connectivity, enhance user experience, and drive innovation.
Watch ‘Introduction to 6G (6th Generation Mobile System)’ Video on YouTube: ![]() https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bQ1ojIO-JyQ
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bQ1ojIO-JyQ
I am hoping that you find this information about 3GPP and its Mobile Technologies is useful and helps further to enhance your understanding.
I am happy to receive your inputs/feedback and looking forward to bring more such engaging content in future.