-
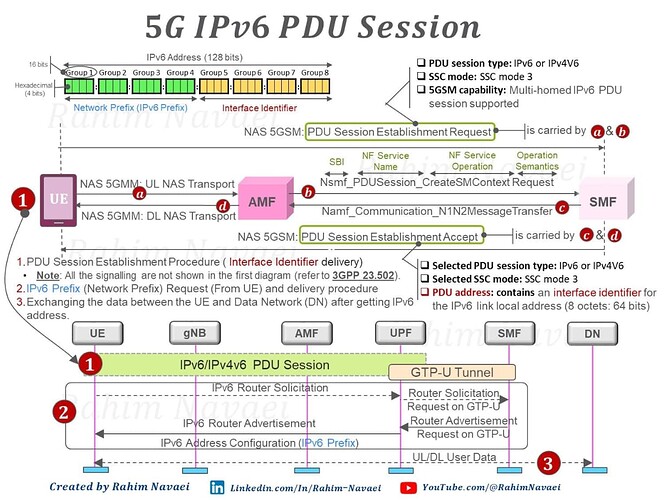
The 5G System supports the IP, Ethernet and Unstructured. PDU Session to exchange the user packets . In the case of an IP PDU Session, the 5G device can request the network to establish an IPv4, IPv6 or IPv4V6 PDU Session using “ PDU Session Type Information Element ” within the “ PDU Session Establishment Request “ message .
-
The SMF (Session Management Function) within the 5G Core assigns the IP address for the 5G device. In the case of an IPv4/IPv4v6 PDU Session, the IPv4 address is delivered to the 5G device using “ PDU address Information Element ” within the “ PDU Session Establishment Accept “ message. The IPv6 address delivery process is different.
-
An IPv6 address is composed of two parts:
- Network prefix (IPv6 Prefix): It consists of n bits and has the same function as the network Identifier of an IPv4 address.
- Interface Identifier: It consists of (128 – n) bits and is parallel to the host ID of an IPv4 address
-
“Interface Identifier “ is delivered via the NAS message using “PDU address IE” .
-
“IPv6 Prefix” is not carried by the NAS message. It is provided by the SМF and then sent to the 5G device after establishing the PDU Session using an ‘IPv6 Router Advertisement’ message (specified by IETF RFC 4861). This message is sent to the 5G device through the N4-U coппection (between the SMF and UPF) and N3 (between the UPF and gNB) using GTPv1-U ( GPRS Tunneling Protocol version one User Plane).
![]() Here I am trying to depict the IPv6 address structure and how the two parts of the IPv6 address are delivered to the 5G device.
Here I am trying to depict the IPv6 address structure and how the two parts of the IPv6 address are delivered to the 5G device.
LinkedIn: ![]()