Efficient frame structure is crucial for managing data transmission across a much faster and more flexible wireless networks. Key components:
-
Frame:
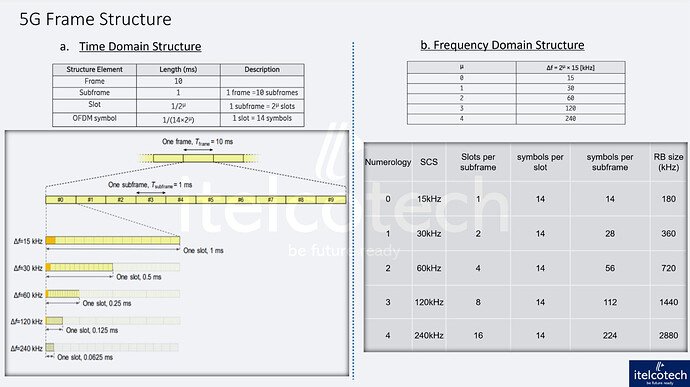
- In 5G, the frame duration is also 10 ms
- It consists of 10 subframes, each of 1 ms.
-
Subframe:
- 1 ms long and contains a varying number of slots basis subcarrier spacing
- With flexible subcarrier spacing (15 kHz to 240 kHz), the number of slots per subframe can change (e.g., 1 slot for 15 kHz, 2 slots for 30 kHz, etc.).
- Subframes are critical for scheduling, can prioritize control information.
-
Slot:
- The slot duration varies based on the subcarrier spacing:
- For 15 kHz spacing, a slot is 1 ms long
- For 30 kHz spacing, a slot is 0.5 ms, and so on.
- Each slot contains 14 OFDM symbols (with normal cyclic prefix)
- The slot duration varies based on the subcarrier spacing:
-
Resource Block (RB):
- Number of subcarriers over one slot
- RB size vary basis subcarrier spacing of 15, 30, 60, 120, or 240 kHz.
e.g., 30 kHz spacing - RB spans 360 kHz (12 subcarriers × 30 kHz)
-
Resource Element (RE):
- Smallest unit of data transmission - one subcarrier in frequency domain and one OFDM symbol in the time domain.
-
Numerology and Scaling:
- Different numerologies are used basis service or deployment scenario:
- 15 kHz spacing widely used in lower frequency bands.
- 30 kHz, 60 kHz, and beyond allow for faster data rates and shorter slot durations, ideal for higher frequency bands and low-latency applications.
- Different numerologies are used basis service or deployment scenario:
Note - There are 489/960kHz subcarriers also, but rarely used.
LinkedIn: ![]()