-
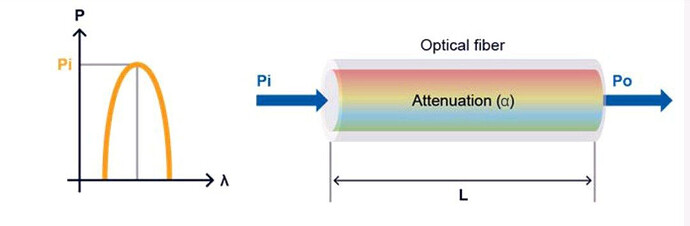
Attenuation is the amount of light loss from input to output.
-
Attenuation can be classified to intrinsic and extrinsic.
-
Intrinsic attenuation is absorption of light energy and scattering.
-
Intrinsic depends on the fiber impurities.
-
Extrinsic attenuation is the fiber bending , strees from manufacturing and other environmental factors.
-
Total link loss = fiber loss + connectors loss + splice loss.
-
Fiber loss = 10 log output power / input power.
-
Fiber attenuation represented in db./ km.
-
Attenuation can be from 0.2-0.3 db / km in SMF ( single mode ) G652 for C band ( 1550 nm ) as an example.
-
Fiber loss depends on fiber length , fiber type and wavelength of signal.
-
All passive equipments like attenuators and dispersion compensation devices can Introduce insertion loss.
-
DCM is dispersion compensation modules, it’s used to solve pulse broadening issue.
-
dispersion can be chromatic or polarization.
-
dispersion value can be expressed by
PS / km.nm
LinkedIn: ![]()