-
They’re 2 main types of Tx impairments: linear and non linear.
-
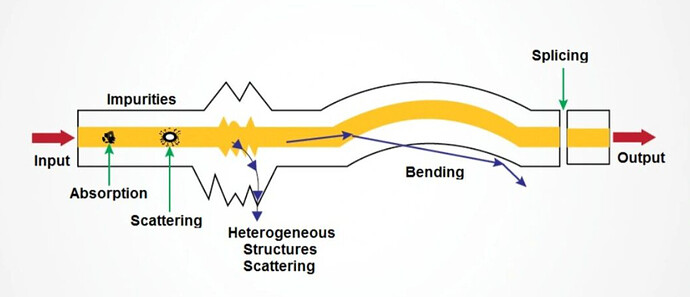
Most important impairment in optical networks is attenuation.
-
Attenuation represent the amount of light loss in Tx medium between input and output.
-
Attenuation has 2 main sources : absorption and scattering.
-
In absorption there’s some optical energy lost due to glass impurities and atomic defects.
-
Scattering is a light loss due to disperse optical energy in random directions inside the cable due to variations of the density/ concentration of fiber core.
-
Extrinsic attenuation caused by physical pending of fiber , stretching , physical stress from underground vibrations.
-
Fiber loss can be calculated by:
- 10 log P out / P input
-
When you need to calculate link loss you should consider :
- Fiber loss + connector loss + splices loss
-
Attenuation represented in dB / km
-
Insertion loss is the loss introduced by passive components like dispersion compensation modules , demultiplexers , attenuators
-
CD : chromatic dispersion
-
This is a pulses overlapping occured in optical networks due to that the different optical signals travel with different speeds
-
CD cause ISI ( intersymbol interference )
-
CD measured by PS / NM . KM
-
CD solved by dispersion compensation modules
-
PMD : polarization mode dispersion
-
PMD is another type of dispersion that’s caused by asymmetrical fiber core , if we have 2 orthogonal optical signals vertical and horizontal
-
PMD cause the 2 orthogonal signal nV * H to travel the Fiber cable with 2 different group velocities which causes the 2 signals received with different times
-
PMD caused mainly by imperfect circular fiber core and varies by external stress like lay the fiber close to train and high vibrations environments
LinkedIn: ![]()