Believe us: it is not so easy to get an up-to-date list of all cells in the network, including some most important parameters.
But this can be easily achieved through Boda’s CM module, specifically the Key Parameters.
Boda Key Parameters is a very useful special report, pre-loaded with Boda installation.
Once you have imported all your CM raw dump into Boda, it’s already there available to you, via pre-loaded queries.
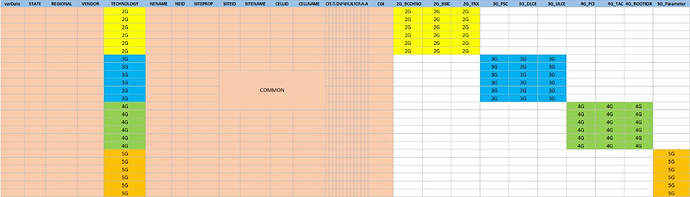
It’s basically a table, so let’s take a quick view on each field.
- FIELD: name of the field
- TYPE: is this field common to all RAT, os specific to only a specifi RAT?
- SOURCE: does it come from CM Dump, or from other auxiliary input?
- DESCRIPTION: basic description of the fiield.
| FIELD | TYPE | SOURCE | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| varDate | Common | CM Dump | Date time information, from raw dump for each cell |
| STATE | Common | Auxiliar (Input) | |
| REGIONAL | Common | Auxiliar (Input) | |
| VENDOR | Common | CM Dump | Vendor (Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, ZTE, etc.) |
| TECHNOLOGY | Only for Specific RAT | CM Dump | Technology (2G, 3G, 4G, 5G) of the cell |
| NENAME | Common | CM Dump | Grouping Network Element - NE (BSC/RNC for 2G/3G; MME for 4G; ANF FOR 5G) |
| NEID | Common | CM Dump | Id of the grouping NE |
| SITEPROP | Common | CM Dump | Physical Property, site location |
| SITEID | Common | CM Dump | Id of SITE |
| SITENAME | Common | CM Dump | Name of the SITE |
| CELLID | Common | CM Dump | Id of the cell |
| CELLNAME | Common | CM Dump | Name of the cell |
| CI | Common | CM Dump | Local Cell ID |
| ACTSTATUS | Common | CM Dump | Active Status (Activated, Deactivated) |
| BLKSTATUS | Common | CM Dump | Blocked Status (Blocked, Unblocked) |
| DLBANDWIDTH | Common | CM Dump | Downlink Bandwidth (MHz) |
| BAND | Common | CM Dump | Frequency (BAND) |
| CARR | Common | CM Dump | Carrier |
| DLF | Common | CM Dump | Downlink Frequency (ARFCN) |
| ULF | Common | CM Dump | Uplink Frequency (ARFCN) |
| MCC | Common | CM Dump | Mobile Country Code of the cell. The Mobile Country Code (MCC) consists of three decimal digits and the mobile network code consists of two or three decimal digits (for example: MNC of 001 is not the same as MNC of 01). An MCC is used in combination with an MNC (a combination known as an “MCC/MNC tuple”) to uniquely identify a mobile network operator (carrier) using the GSM (including GSM-R), UMTS, LTE, and 5G wireless networks. |
| MNC | Common | CM Dump | Mobile Network Code of the cell. The Mobile Network Code (MNC) is a unique 2-digit number to identify a mobile network. It is used within the International Mobile Subcriber Identity (IMSI) to uniquely identify mobile subscribers and within a Location Area Identification (LAI)to uniquely identify a location area within the mobile network. |
| LAC | Common | CM Dump | LAC of the cell (Both the LAC and TAC share the same concept of providing the location code of a base station set. The only difference between LAC and TAC is that the LAC is the terminology used in GSM/UMTS while the TAC is the terminology used in LTE.) |
| RAC | Common | CM Dump | RAC of the cell. The Routing Area Code (RAC) combines an integer value between 0 and 255 defined inside a LA. The routing area identity (RAI), defined by an operator, identifies one or several cells. |
| CGI | Common | CM Dump | The Cell Global Identification (CGI) is used in GSM/UMTS standard and it is defined as the concatenation of the MCC (Mobile Country Code), MNC (Mobile Network Code), LAC (Location Area Code) , and the CI (Cell Identity). In LTE it is the eCGI. |
| 2G_BCCHNO | Only for 2G cells | CM Dump | A Broadcast Control Channel (BCCH) is a point to multipoint, unidirectional (downlink) channel used in the Um interface of the GSM cellular standard. The BCCH carries a repeating pattern of system information messages that describe the identity, configuration and available features of the base transceiver station (BTS). These messages also provide a list of absolute radio-frequency channel numbers (ARFCNs) used by neighboring BTSs |
| 2G_BSIC | Only for 2G cells | CM Dump | The Base Sstation Identity Code (BSIC) is a code used in GSM to uniquely identify a base station. The code is needed because it is possible that mobile stations receive the broadcast channel of more than one base station on the same frequency. |
| 2G_TRX | Only for 2G cells | CM Dump | Number of TRX of the cell. A TRX transmits and receives according to the GSM standards, which specify eight TDMA timeslots per radio frequency, to serve several different frequencies and different sectors of the cell. This information allows the handsets to identify the network and gain access to it. This signalling makes use of a channel known as the Broadcast Control Channel (BCCH). |
| 3G_PSC | Only for 3G cells | CM Dump | Primary Scrambling Code for 3G Cells. The PSC is a set of 512 scrambling codes used to, well, scramble downlink transmissions so the UE can distinguish signals from different cells. |
| 3G_DLCE | Only for 3G cells | CM Dump | Number of Downlink Channel Elements. A channel element (CE) is defined as the baseband resources required in the Node B. On the RNC side, it is referred to as the NodeB credit. On the NodeB side, it is referred to as the Channel Element (CE). |
| 3G_ULCE | Only for 3G cells | CM Dump | Number of Uplink Channel Elements. A channel element (CE) is defined as the baseband resources required in the Node B. On the RNC side, it is referred to as the NodeB credit. On the NodeB side, it is referred to as the Channel Element (CE). |
| 4G_PCI | Only for 4G cells | CM Dump | Physical Cell ID (PCI) is one of the most important cell’s identifier in the wireless network of LTE system. The PCI is a set of 504 IDs (derived from 3 primary synch sequences and 168 secondary sequences) used to scramble certain downlink transmissions so the UE can distinguish signals from different cells. |
| 4G_TAC | Only for 4G cells | CM Dump | TAC - Tracking Area code is an essential part of the tracking area (TA) identity. Each eNodeB consists of one or more cells. The set of several eNodeB constitutes a tracking area. Each tracking area has a unique code called as the tracking area code. The tracking area code is a 16 bit number and is made through eNodeB code. |
| 4G_ROOTIDX | Only for 4G cells | CM Dump | The Root Sequence Index is broadcast as part of PRACH configuration in SIB 2 of the LTE cell. This allows the UE to calculate which PRACH preamble it can use to attach to the cell. The PRACH preambles are Zadoff-Chow sequences of 838 length. The UE calculates the preamble by applying a cyclic-shift on this Root Sequence Index. |
Note: in the current version, Boda Lite present Key Parameters as separate queries. Next releases will have a query concatenating it all (all cells for all RAT) in one single table.
Resources
- Boda Quick Reference Guide Boda Quick Reference Guide