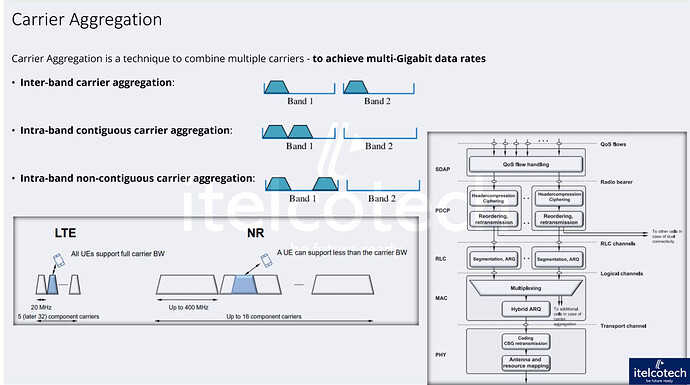
Carrier Aggregation (CA) is a key technique enabling wireless networks to achieve blazing-fast multi-Gigabit data speeds by combining multiple carriers. It enhances both bandwidth and performance, delivering an unparalleled experience in data rates and network capacity.
Did you know?
-
LTE supports up to 5 carrier components of 20 MHz each (later expanded to 32 carriers).
-
5G takes it further, supporting up to 16 carriers with a maximum of 400 MHz bandwidth.
-
Carrier Aggregation operates at Layer 2 of the protocol stack, specifically at the MAC layer, ensuring optimal data throughput.
Here are the types of Carrier Aggregation:
-
Inter-band Carrier Aggregation: Combines carriers across different frequency bands, maximizing spectrum use for increased capacity.
-
Intra-band Contiguous Carrier Aggregation: Aggregates adjacent carriers within the same band, ensuring efficient spectrum usage.
-
Intra-band Non-contiguous Carrier Aggregation: Aggregates carriers within the same band that are not adjacent, enhancing flexibility in spectrum utilization.
Note - Number of carrier components depends upon spectrum allocation and ecosystem development.
LinkedIn: ![]()