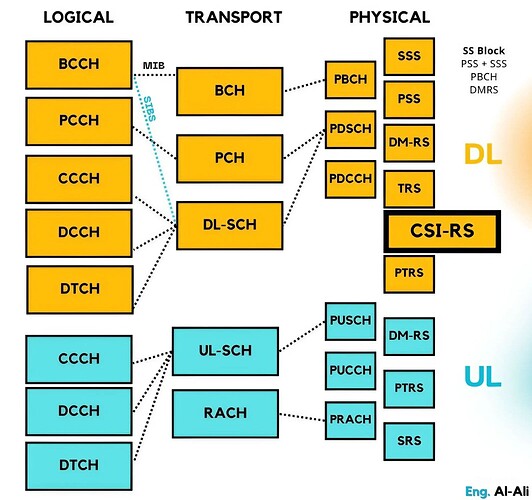
Did you know CSI-RS (Channel State Information - Reference Signal) first appeared in LTE Release 10 and now plays a critical role in 5G? In 5G, CSI-RS helps optimize downlink performance once a PDSCH is allocated, ensuring smooth connectivity.
Functions of CSI-RS in 5G:
- Link Adaptation: The gNB transmits CSI-RS, and the UE measures it, reporting vital parameters like CQI, PMI, RI, and SS/PBCH Block Resource Indicator (SSBRI).
- Radio Link Monitoring (RLM): Supports link state monitoring, ensuring stable connections with help from SSB signals.
- Radio Resource Management: Crucial for handovers, guiding the process by providing real-time channel data.
- Beamforming: Essential for focused signal transmission and beam management to enhance signal quality.
- Radio Link Failure Detection: CSI-RS helps detect in-sync and out-of-sync conditions, ensuring the link stays operational.
- Beam Failure Detection & Recovery: Assists in monitoring beam health and recovering from beam failures when conditions degrade.
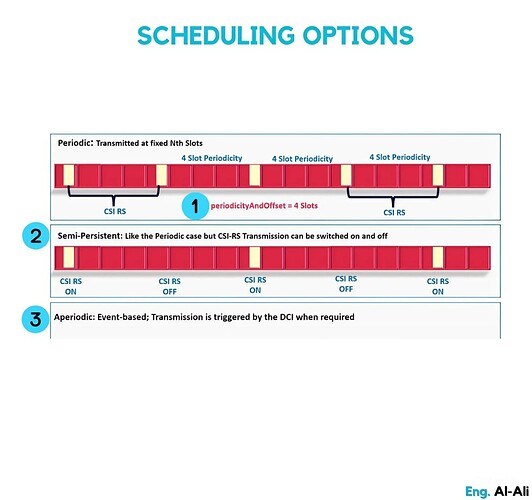
Scheduling Options:
CSI-RS can be transmitted in periodic, semi-persistent, or aperiodic modes based on network conditions.
- Periodic: The gNodeB periodically transmits CSI-RS to UEs by the configured period, and UEs receive CSI-RS in the same period.
- Semi-persistent: This is the same as periodic, but transmission can be momentarily suspended.
- Aperiodic: Transmission happens without a pre-defined schedule. UE has to be notified of such transmission with downlink control information or DCI.
CSI-RS Types:
- Non-Zero Power (NZP): Used for channel measurement, beam management, and mobility, as well as managing intra-cell interference in Multi-User MIMO.
- CSI Interference Measurement (CSI-IM): Measures inter-cell interference from neighboring cells during SU-MIMO.
- Zero Power (ZP): Defines rate-matching patterns, avoiding interference on specified resource elements.
Note: In the uplink, the SRS channel performs similar functions.
That’s it ![]()
LinkedIn: ![]()