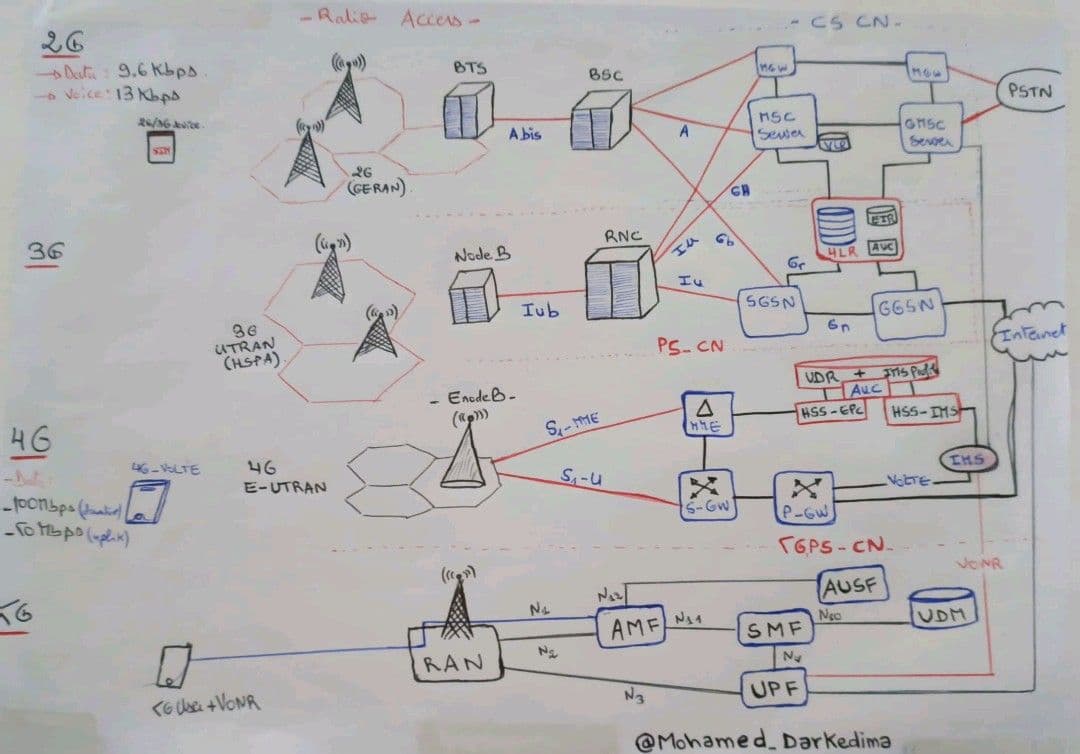
Find below a Summarized description for every Radio Access Technology.
![]() 2G
2G
2G or second-generation wireless technology was introduced in the 1990s. It uses a circuit-switched network architecture that divides the radio spectrum into several channels. The 2G network architecture comprises three main components:
![]() Mobile Station (MS): This includes the mobile phone and the SIM card.
Mobile Station (MS): This includes the mobile phone and the SIM card.
![]() Base Station Subsystem (BSS): This includes the Base Transceiver Station (BTS) that communicates with the mobile phone and the Base Station Controller (BSC) that manages the allocation of radio channels.
Base Station Subsystem (BSS): This includes the Base Transceiver Station (BTS) that communicates with the mobile phone and the Base Station Controller (BSC) that manages the allocation of radio channels.
![]() Network Switching Subsystem (NSS): This includes the Mobile Switching Center (MSC) that manages the switching of calls between different networks, and the Home Location Register (HLR) that stores user data.
Network Switching Subsystem (NSS): This includes the Mobile Switching Center (MSC) that manages the switching of calls between different networks, and the Home Location Register (HLR) that stores user data.
![]() 3G
3G
3G or third-generation wireless technology was introduced in the early 2000s. It uses a packet-switched network architecture that enables faster data transfer rates and supports multimedia applications. The 3G network architecture comprises four main components:
![]() User Equipment (UE): This includes the mobile phone or any other device that accesses the internet.
User Equipment (UE): This includes the mobile phone or any other device that accesses the internet.
![]() Radio Access Network (RAN): This includes the Node B that communicates with the UE and the Radio Network Controller (RNC) that manages the allocation of radio resources.
Radio Access Network (RAN): This includes the Node B that communicates with the UE and the Radio Network Controller (RNC) that manages the allocation of radio resources.
![]() Core Network (CN): This includes the Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) that manages the routing of data packets and the Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN) that acts as the interface between the mobile network and the internet.
Core Network (CN): This includes the Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) that manages the routing of data packets and the Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN) that acts as the interface between the mobile network and the internet.
![]() 4G
4G
4G or fourth-generation wireless technology was introduced in the late 2000s. It uses an all-IP (Internet Protocol) network architecture that enables faster data transfer rates and supports high-bandwidth applications such as video streaming and online gaming. The 4G network architecture comprises four main components:
![]() User Equipment (UE): This includes the mobile phone or any other device that accesses the internet.
User Equipment (UE): This includes the mobile phone or any other device that accesses the internet.
![]() Evolved Packet Core (EPC): This includes the Serving Gateway (SGW) that manages the data flow between the UE and the network, the Packet Data Network Gateway (PDN GW) that provides access to the internet, and the Mobility Management Entity (MME) that handles signaling between the UE and the network.
Evolved Packet Core (EPC): This includes the Serving Gateway (SGW) that manages the data flow between the UE and the network, the Packet Data Network Gateway (PDN GW) that provides access to the internet, and the Mobility Management Entity (MME) that handles signaling between the UE and the network.
![]() Radio Access Network (RAN): This includes the eNodeB that communicates with the UE and the Evolved Node B Gateway (eNB GW) that manages the allocation of radio resources.
Radio Access Network (RAN): This includes the eNodeB that communicates with the UE and the Evolved Node B Gateway (eNB GW) that manages the allocation of radio resources.
![]() Home Subscriber Server (HSS): This stores the subscriber data and provides authentication and authorization services.
Home Subscriber Server (HSS): This stores the subscriber data and provides authentication and authorization services.
Linkedin (Credits): ![]()