EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) uses a composite metric to select the best path based on factors like link speed (bandwidth) and the time it takes for data to travel (delay). These are controlled by settings called K-values.
The metric calculation relies on these K-values, which can be adjusted to influence routing decisions. The default K-values are:
- K1 (Bandwidth)
- K2 (Load)
- K3 (Delay)
- K4 (Reliability)
- K5 (MTU)
Typically, only K1 (Bandwidth) and K3 (Delay) are used in most EIGRP configurations, with K2, K4, and K5 disabled by default. EIGRP selects the best path based on the lowest bandwidth link in the path and total delay of all routers.
The EIGRP metric using the default K-values is calculated using the formula:
Metric = 256 * (10^7 / Lowest Bandwidth Link) + (Sum of Delay / 10)
Understanding how EIGRP’s metric and K-values work allows you to optimize routing decisions and gain more control over how paths are chosen in your network.
Try exploring how EIGRP’s metric calculation influences routing decisions in your network!
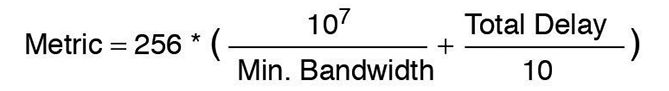
LinkedIn: ![]()