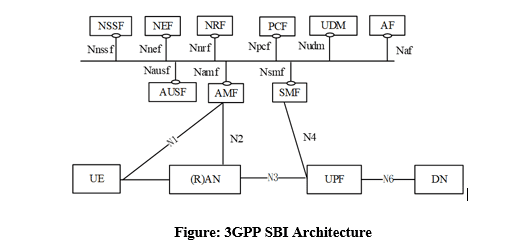
NRF (Network Repository Function) facilitates cloud-native 5G networks by enabling dynamic and efficient discovery of peer Network Functions, enhancing scalability.
Introduction:
DNS (Domain Name Service) has been widely used by networks to discover 3G and 4G Network Functions (NFs).
Every time there is a change in the network, this entails adding or updating records in the DNS server. This solution was not cohesive.
The 5G Network Repository Function (NRF), which was introduced in the 5G specification, addresses this issue. Every Network Function needs to register its profile with NRF when it's ready to service the APIs. Every NF type contains unique information in the NF profile.
For example, Session Management Function (SMF) might provide the set of Data Network Names (DNN) it serves. One thing to note is that SMF may still choose User Plane Function (UPF) using proprietary logic because the UPF interface to NRF is still optional.
In this article we shall see various advantages provided by 3GPP’s NRF network function over traditional 3G/4G networks.
Continue reading: ![]()