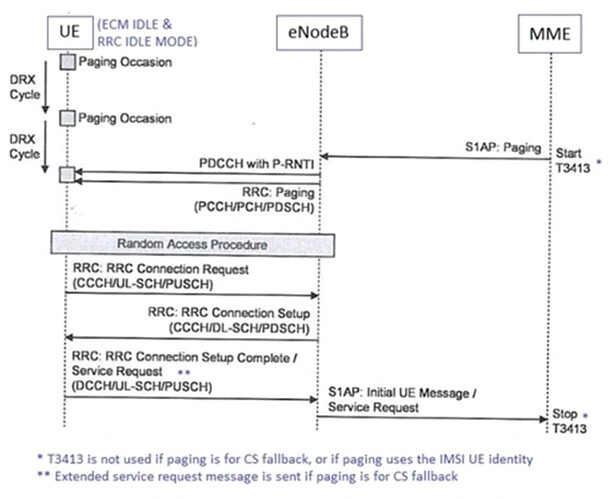
Stepwise approach to Paging

The LTE paging procedure is applicable to UE in ECM IDLE State. UE in this state are in RRC IDLE mode and do not have S1 connectivity with MME.
The location of a UE in ECM IDLE state is known by MME on a per tracking area basis. The MME has to forward S1AP paging message to all eNodeB within the relevant tracking area.
MME forward paging message to multiple eNodeBs as UE can be registered with more than a single tracking area.
-
MME starts timer T3413 after sending S1AP paging message for PS data call and LTE UE is addressed by S-TMSI instead of IMSI.
-
eNodeB receives S1AP paging message from MME and constructs RRC paging message. Single RRC can carry information from multiple S1AP. Paging message can include multiple paging records to page multiple UE. Table-2 below mentions contents and structure of RRC paging message.
-
UE in RRC IDLE mode checks for paging once every DRX cycle. paging occasion within the paging frame defines specific subframe during which a LTE UE checks for paging message.
-
UE searches forP-RNTI within PDCCH of subframe belong to paging occasion. P-RNTI has value of FFFE and indicates that UE may have a paging message on PDSCH.
-
UE finds P-RNTU in PDCCH, it will decode resource allocation information.
-
This information directs UE to PDSCH RB where in paging message has been sent.
-
UE decodes RRC message from PDSCH RBs and checks UE identity in all the records. If UE do not find its identity in paging record then it will return to check PDCCH for P-RNTI at each of the paging occasions.
-
If the UE find its identity, it will trigger random access procedure to establish RRC connection.
-
UE sends RRC connection request message and eNodeB responds with RRC connection setup message.
-
If the LTE paging procedure is for PS data call, UE includes service request NAS message within RRC connection setup complete message.
-
If the paging procedure is for CS fallback call, UE includes extended service request NAS message within RRC connection setup complete message.
-
The eNodeB forwards NAS message to MME which will stop T3413 if it is running and will proceed to establish connection with UE.
-
A paging retransmission will be triggered if T3413 gets expire prior to MME receiving a NAS message from UE.
-
UE checks for RRC paging message for SI modification flag and ETWS flag. If the former is present UE reacquires BCCH SI. If the later is present, UE reads ETWS notifications in SIB10 and/or SIB11.
Purpose of Paging Procedure
-
To transmit paging information to a UE in RRC_IDLE state.
-
To inform UEs in RRC_IDLE and UEs in RRC_CONNECTED state about a system information change.
-
To inform UE about ETWS primary notification and ETWS secondary notification.
-
To inform CMAS notification.
When RRC layer receives paging it notify upper layer about this. Upper layer may request RRC to establish RRC connection as a response of paging.
IEs in PAGING message
-
CN-Domain: Indicates the origin of paging (ps or cs).
-
UE-Identity: Provides the NAS identity of the UE that is being paged (S-TMSI or IMSI).
-
SystemInfoModification: If present, this IE indicates a BCCH modification other than SIB10, SIB11 and SIB12.
-
etws-Indication: If present, this IE indicates an ETWS primary notification and/or ETWS secondary notification.
-
cmas-Indication: If present, this IE indicates a CMAS notification
Action by UE after receiving Paging Info
-
If UE receives paging in RRC_IDLE state if UE Identity included in the paging record matches with UE identities assigned by upper layer then UE RRC (Radio Resource Control) needs to forward ue-Identity and cn-Identity to upper layer.
-
If UE receives paging with request to modify system information (systemInfoModification) then reacquire the required system information.
-
If UE is ETWS capable and received etws-Indication in paging message, UE needs to re-acquire SIB 1 immediately. If schedulingInfoLost IE indicates that SIB 10 is present then RRC will acquire SIB 10 otherwise if SIB 11 is present then RRC will read SIB 11.
-
Similarly when smas-Indication is included in paging message, RRC will re-acquire SIB 1 immediately. If schedulingInfoList indicates that SIB 12 is present then RRC layer will acquire SIB 12.