-
QoS is Quality of Service.
-
It aims to forward traffic efficiently and perform bandwidth utilization.
-
QoS used to classify traffic and assign specific priorities and forward the traffic based on priorities.
-
It helps handling real time traffic, voice and video efficiently and even data traffic.
-
QoS works with L2 and L3 frames and packets.
-
WDM and optical devices L2 cards support Qos protocols.
-
QoS has 4 processes :
- Classification
- Mmarking / policing
- Queing
- Scheduling
-
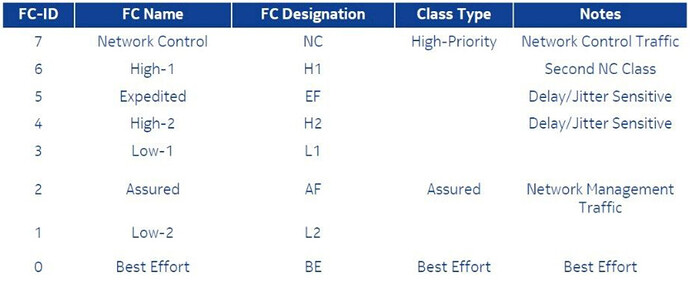
Classification means assign forwarding class for each traffic flow depends on types of information carried by packet, we have 8 forwarding class based on importance and type of traffic.
-
Policing means control bandwidth used by each traffic flow, identify whether the income traffic is over , below or within the committed rate.
-
Policing called coloring, we have colors for the packets.
- Red : if the incoming packet bandwidth is greater than the peak Information rate ( in that case we have to discard )
- Yellow : if the rate of packet is between the peak and committed data rate , in that case we will discard the packet only if congestion occurred
- Green : if the bandwidth is lower than the committed rate , in that case the packet Forwarded normally
-
Queing means put the traffic in it’s specific Queue , FIFO is First in First out , move the packet from ingress to egress Ports.
-
It’s about how to order packets into the egress buffer memory.
-
Scheduling means select the SLA ( service Level agreement ) for each packet , we have different schedulers types as below.
- Strict priority
- Round robin
- Weighted round robin
- Weighted deficit round robin
LinkedIn: ![]()