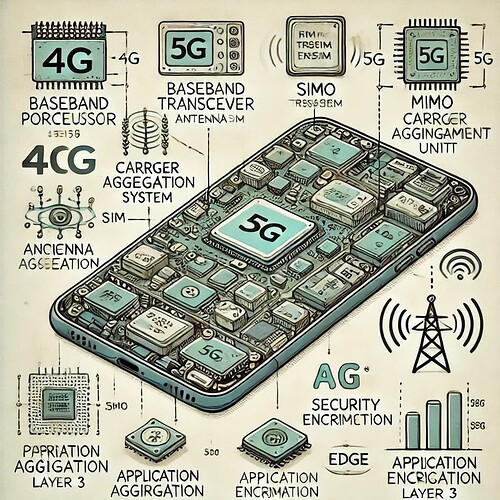
Inside the UE: How Your Device Communicates with the Network
Ever wondered what’s inside your smartphone or modem that enables seamless communication with 4G and 5G networks? User Equipment (UE) is packed with advanced hardware and software that ensure connectivity, speed, and security. Here’s a deep dive into the key components that make it all happen!
-
Core Components of UE:
- Baseband Processor (BBP): Handles signal processing and cellular protocols (LTE, 5G NR).
- RF Transceiver & Antenna System: Converts signals for transmission and reception.
- SIM/USIM/eSIM: Stores authentication credentials for network access.
- Application Processor (AP): Runs the OS and apps.
- Power Management Unit (PMU): Optimizes energy consumption.
- Protocol Stack: Includes Layer 1 (Physical), Layer 2 (MAC, RLC, PDCP), and Layer 3 (RRC, NAS) for network communication.
-
Advanced Components Enhancing Connectivity:
- MIMO & Beamforming: Improves signal strength and data rates.
- Carrier Aggregation & Dual Connectivity: Enables faster speeds by combining frequency bands.
- AI-Based Optimization: Enhances network selection, beam management, and power efficiency.
- Security Enhancements (TPM, eSIM): Ensures data encryption and secure authentication.
- Energy Efficiency Features (DRX, Dynamic Power Scaling): Extends battery life.
- Edge Computing Support (MEC): Reduces latency by processing data closer to the user.
From basic signal transmission to AI-driven network optimization, modern UEs are engineered for speed, reliability, and efficiency. As 5G evolves, we’ll see even more innovations shaping the future of mobile connectivity.
LinkedIn: ![]()