Hello dears.
It’s a very well explained and very informative video, showing important concepts in 1-hour session.
You will step through the life of a MR-DC capable 5G UE in your deployed network of 5G Non-Standalone (NSA) network so you are better equipped to operate and monitor performance of your network.
Enjoy.
This is the link for this video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p8ruJm8agBQ
And you may also see other (good) videos in the channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCFoinxSIohSgNkPTVd17Smw
2 Likes
Introduction
In the era of 5G, the journey of a User Equipment (UE) in a Non-Standalone (NSA) 5G network is both fascinating and technically complex. NSA architecture, which leverages existing LTE infrastructure, represents the initial phase of 5G deployment. It enables UE to experience higher data rates and lower latency while still relying on LTE for control signaling.
-
UE Power-On and Cell Search
The journey begins when the UE powers on and starts searching for a network:
Cell Search: The UE scans for available LTE cells in its vicinity using synchronization signals (SS) and system information blocks (SIBs).
Attach to LTE: Once an LTE cell is identified, the UE attaches to it as its primary connection point.
-
Initial NAS Signaling via LTE
In NSA, LTE serves as the anchor for all signaling procedures:
Attach Request: The UE sends an Attach Request to the LTE eNodeB, which forwards it to the core network.
Authentication and Security: The LTE network performs authentication, establishes encryption, and sets up secure channels for communication.
-
5G Capability Negotiation
To enable 5G services:
The UE shares its capability information with the LTE eNodeB, indicating its support for NR (New Radio).
The LTE network coordinates with the 5G gNodeB to verify and activate the UE’s 5G capabilities.
-
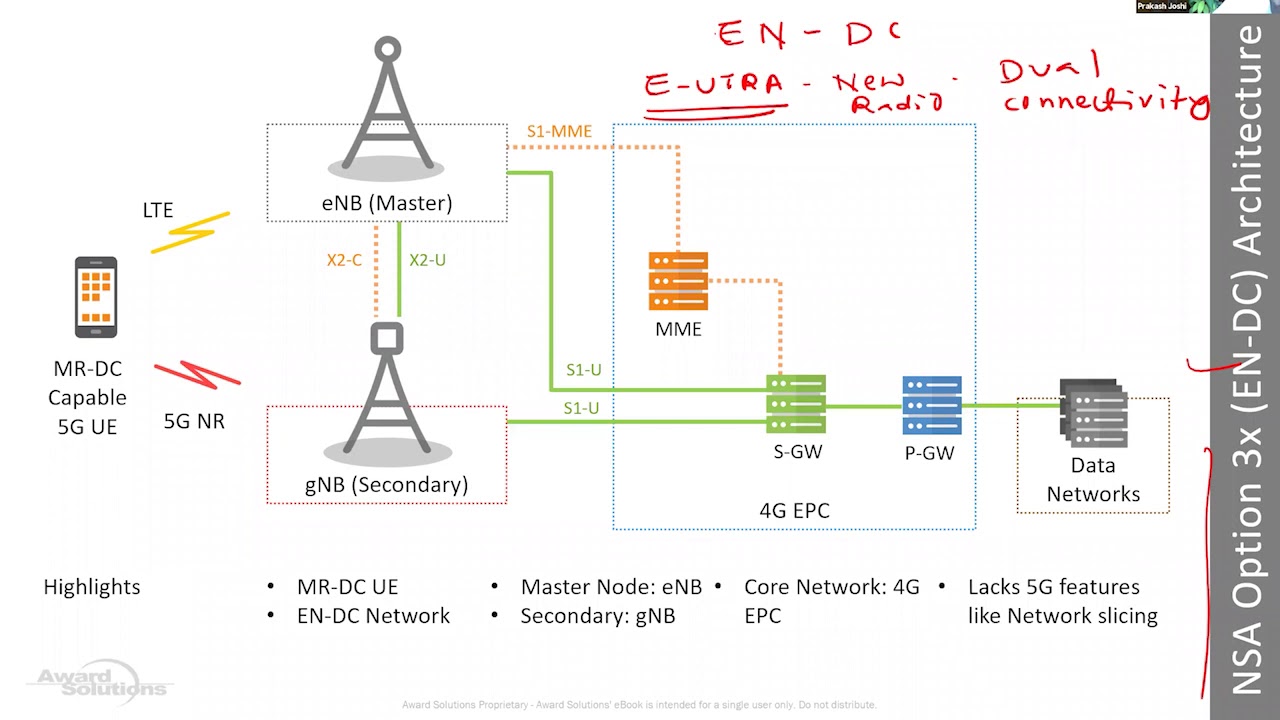
Dual Connectivity Setup (EN-DC)
Under NSA, dual connectivity is established between LTE and 5G:
Master Cell Group (MCG): LTE serves as the primary connection point.
Secondary Cell Group (SCG): 5G NR is added as a secondary link for enhanced data throughput.
The UE establishes two bearers:
Control Plane Bearer: Handled by LTE.
User Plane Bearer: Split across LTE and 5G NR for optimized data transfer.
-
5G NR Data Transmission
Once the dual connectivity is active, the UE begins utilizing 5G NR for high-speed data:
Split Bearer: Data traffic is intelligently split between LTE and 5G NR based on network policies and conditions.
Beamforming: The UE communicates with the 5G gNodeB using beamforming for improved signal strength and reliability.
-
Handover Management
Mobility is a critical aspect of the UE’s life in an NSA network:
Intra-RAT Handover: Between LTE cells within the same eNodeB.
Inter-RAT Handover: Between LTE and 5G NR cells.
The UE ensures seamless connectivity by coordinating with both LTE and 5G base stations.
-
Measurement and Reporting
To maintain optimal performance:
The UE continuously measures signal strength, SINR, and other KPIs for both LTE and NR.
Reports are sent to the LTE eNodeB, which manages the overall network resources.
-
Disconnection and Idle Mode
When the session ends or the UE becomes inactive:
Idle Mode Transition: The UE disconnects from the gNodeB but remains registered with LTE.
Context Retention: The UE retains its context to enable fast reattachment when needed.

LinkedIn: