Location Tracking Attacks in 4G (Diameter)
The Diameter protocol is a core component of the 4G/LTE network architecture, primarily used for authentication, authorization, and accounting. Despite its essential role, Diameter is vulnerable to several types of location tracking attacks, which can compromise user privacy and security.
- Types of Location Tracking Attacks
-
Paging Attacks:
- Attackers exploit the paging mechanism used to locate a device for incoming calls or messages.
- By repeatedly initiating paging requests, attackers can track a user’s location based on the responses from the network.
-
Subscriber Information Requests:
- Attackers send fraudulent requests to the Home Subscriber Server (HSS) for user location information.
- These requests can be disguised as legitimate queries, bypassing security checks.
-
Interception of Location Updates:
- Attackers intercept location update messages exchanged between mobile devices and the network.
- This can reveal the geographical area or cell where a device is currently located.
-
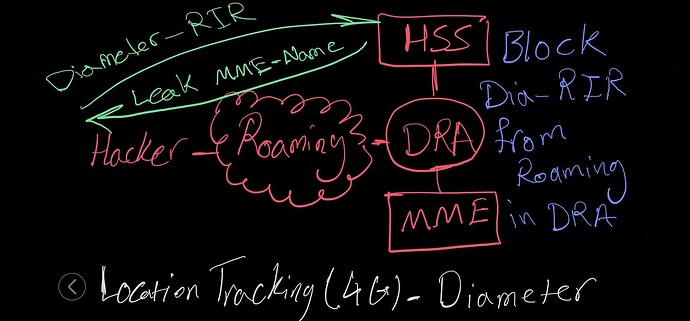
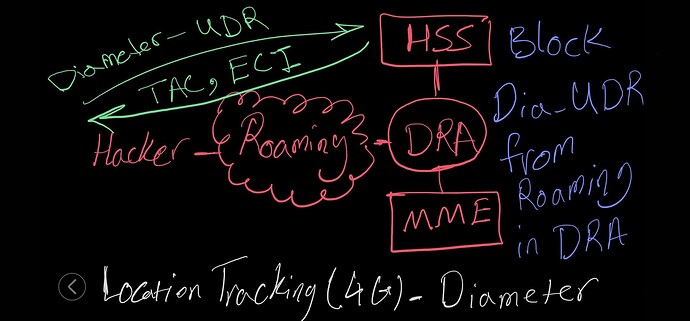
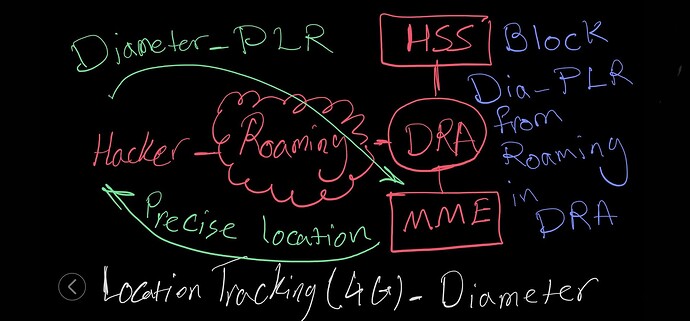
Exploiting Diameter Signaling:
- Diameter signaling messages can be manipulated to obtain location information.
- For instance, attackers can send fake Diameter messages to probe for user location data.
*) Mitigation Strategies
-
Enhanced Authentication and Authorization:
- Implement stringent authentication and authorization mechanisms for Diameter messages.
- Ensure that only trusted entities can send location-related requests.
-
Encryption and Integrity Protection:
- Encrypt sensitive Diameter messages to prevent interception and tampering.
- Use IPsec or TLS to secure Diameter communications, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality.
-
Anomaly Detection Systems:
- Deploy systems to detect unusual patterns in signaling traffic that may indicate an attack.
- Machine learning algorithms can help identify and block suspicious location requests.
-
Network Segmentation:
- Segment the network to limit the exposure of critical components like the HSS.
- Use firewalls and access controls to restrict access to the Diameter infrastructure.
-
Rate Limiting and Throttling:
- Implement rate limiting on paging and location request messages to prevent abuse.
- Throttle requests from sources that exhibit suspicious behavior or high request rates.
-
Regular Security Audits:
- Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments of the Diameter protocol implementation.
- Address identified vulnerabilities promptly through patches and updates.
-
Logging and Monitoring:
- Maintain comprehensive logs of all Diameter signaling messages and activities.
- Monitor these logs in real-time to detect and respond to potential location tracking attacks.
-
User Privacy Policies:
- Adopt strict privacy policies that limit the amount of location data stored and shared.
- Provide users with transparency and control over their location information.
By implementing these strategies, mobile network operators can significantly reduce the risk of location tracking attacks in 4G networks using the Diameter protocol, thereby enhancing user privacy and security.
I hope Your desired points have been cleared. Let me know if you need any other clarification.