-
mmWaves used in 5G networks present challenges such as shorter signal range and increased interference. Due to this, the cell radius in 5G (mmWave) is very small(~300 m) in comparison to 4G (5 to 50 km). As a result, the deployment of 5G can be very expensive and complex since covering a few square kilometers of an area would require numerous gNBs. Moreover, if all gNBs are connected with optical fiber, the complexity and cost further increase.
-
It will be even more challenging if users are moving in a vehicle(poor signal and more interference) so 3GPP is coming up with a solution called Mobile Base Station Relay(MBSR) in 3GPP release 18(2024).
-
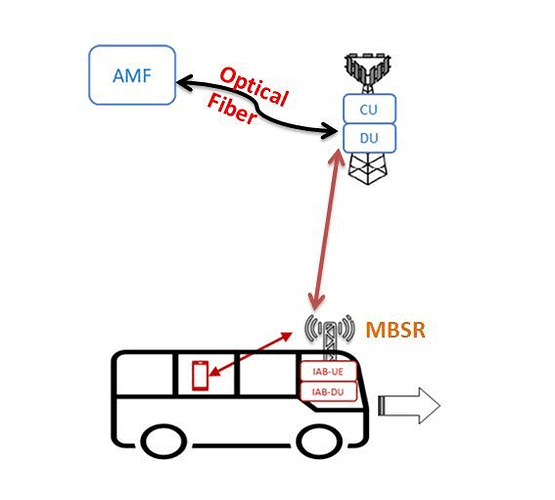
This problem can be solved if somehow gNB is mounted over the vehicles itself and connected with main gNB wirelessly. Users inside the vehicle will always have good signal quality and so best services will be available.
-
MBSR is a mobile base station acts as a relay between a UE and the 5G network, i.e. providing a NR access link to UEs and connected wirelessly (using NR) through a IAB-donor to the 5G Core. It is mounted on a vehicle and serves UEs located inside or outside the vehicle (or entering/leaving the vehicle).
-
Mobile base station relays can be used in scenarios where there are coverage gaps or areas with weak signals, such as rural areas, underground tunnels, or large buildings. They help improve the overall performance and coverage of the mobile network, ensuring a more reliable and seamless communication experience for mobile users.
-
MBSR is using the feature Integrated Access and Backhaul (IAB) introduced in R16.
Integrated Access and Backhaul (IAB):
-
IAB leverages the spectral efficiencies of new radio and the increased capacity afforded by the higher bands available in 5G to deliver an alternative to optical cell site backhaul.
-
Integrated Access and Backhaul specifications define two antenna system types: An IAB node and an IAB donor. IAB Node works as DU(Distributed Unit) while IAB donor have both DU and CU(Centralized Unit).
-
One can think of like if there is a center gNB which is connected with 5G core with fiber and many of gNBs around it are connected wirelessly to it. The center gNB is called IAB donor and gNBs connected with it wirelessly are called IAB Node.
-
In IAB, it is also possible that data for a user can be sent through multiple IAB Nodes before reaching to IAB donor but MBSR have a single hop to the IAB-donor node.
-
By implementing IAB, mobile service providers and private enterprises can extend the coverage and capacity of their 5G networks otherwise It will be more expensive if all these gNBs are connected with optical fiber.
-
With its multi-hop backhauling and decomposed architecture, IAB offers a flexible and cost-effective solution for extending the reach of 5G networks.
Credits: ![]()