QoS Flow in 5G
-
QoS Flow in 5G is equivalent to E-RAB in 4G networks.
-
In 5G, the QoS flow is the finest granularity of QoS differentiation within a Protocol Data Unit (PDU) session.
-
Each QoS flow is identified by a unique identifier called the QoS Flow Identifier (QFI).
-
QoS Flow Types:
-
Guaranteed Bit Rate (GBR) QoS Flow: Provides a guaranteed flow bit rate, typically used for time-critical applications.
- Parameters: Guaranteed Flow Bit Rate (GFBR), Maximum Flow Bit Rate (MFBR), Maximum Packet Loss Rate, and Delay Critical Resource Type.
-
Non-Guaranteed Bit Rate (Non-GBR) QoS Flow: Does not require a guaranteed flow bit rate, typically used for non-time-sensitive applications
- Parameters: Reflective QoS Attribute (RQA), Session-Aggregate Maximum Bit Rate (Session AMBR), and UE-Aggregate Maximum Bit Rate (UE AMBR).
-
Delay Critical Guaranteed Bit Rate (GBR) QoS Flow: Provides latencies significantly lower than guaranteed flow bit rate, typically used in mission-critical applications like automation or intelligent transportation systems.
-
-
QoS Flow Characteristics:
- Resource Type: GBR, Delay-critical GBR, or Non-GBR.
- Priority Level: Determines the forwarding treatment of packets.
- Packet Delay Budget: Maximum allowable delay for a packet.
- Packet Error Rate: Acceptable error rate for the QoS flow.
- Averaging Window: For GBR and Delay-critical GBR resource types.
- Maximum Data Burst Volume: For Delay-critical GBR resource type.
-
QoS Flow Management:
- A PDU Session is a logical connection between the UE and the data network, carrying one or more QoS flows.
- QoS Profile: Contains parameters corresponding to a QoS Flow Identifier (QFI). These profiles are provided by the Session Management Function (SMF) via the Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF) to the 5G RAN.
- QoS Rules are sent to the UE via NAS messages, including QoS parameters and packet filters to map uplink traffic to QoS flows.
- Data Radio Bearers (DRBs) are used to transport QoS flows between the UE and the gNodeB.
- Unlike 4G, multiple QoS flows can be mapped onto the same DRB.
- IP packets are mapped to QoS flows at the Non-Access Stratum (NAS) level, and then QoS flows are mapped to DRBs at the Access Stratum (AS) level.
- The QoS Flow Identifier (QFI) uniquely identifies each QoS flow within a PDU session. The QFI is carried in the encapsulation header on the N3 interface.
- The 5G QoS Identifier (5QI) is a scalar that points to a set of QoS characteristics controlling the packet forwarding treatment. Standardized or pre-configured values are not signaled unless certain QoS characteristics are modified.
- The UPF is responsible for mapping IP packets to QoS flows belonging to a specific PDU session.
- The SMF controls QoS flows and provides QoS profiles.
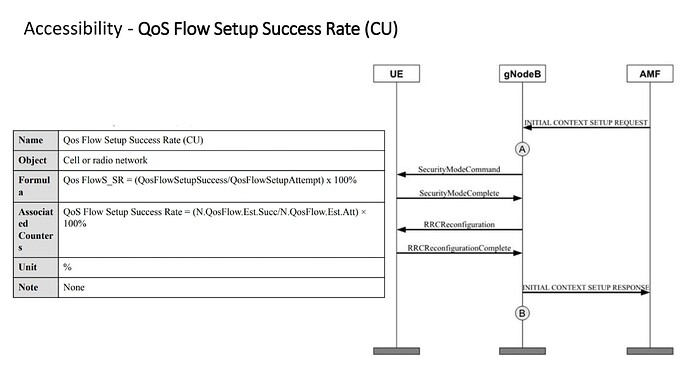
- The QoS Flow Success Rate can be calculated by dividing the QoS Flow Success Establishment over the QoS Flow Establishment Attempts.
LinkedIn: ![]()