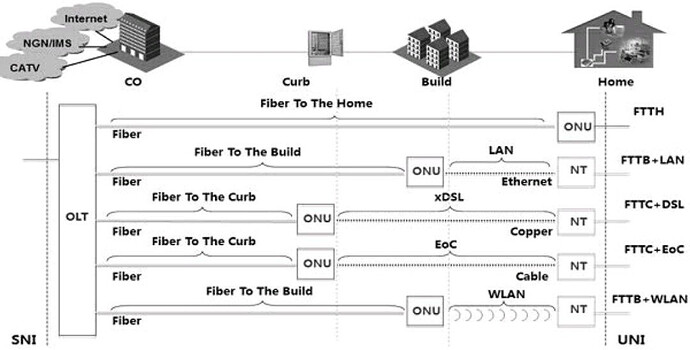
Here are some common terminologies used in Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) networks:
-
Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH): A broadband network architecture that uses optical fiber to deliver high-speed internet, voice, and video services directly to residential and business premises.
-
Optical Fiber: A thin, flexible, and transparent cable made of glass or plastic that transmits data as pulses of light. It forms the backbone of the FTTH network.
-
Optical Line Terminal (OLT): The equipment located at the central office or headend of the FTTH network that serves as the aggregation point for all subscriber connections.
-
Optical Network Unit (ONU)/Optical Network Terminal (ONT): The device installed at the subscriber’s premises to convert optical signals from the OLT into electrical signals for use with computers, phones, and other devices.
-
Drop Cable: A fiber optic cable that connects the distribution network to individual subscriber premises. It is used for the final connection in FTTH deployments.
-
Distribution Cable: A fiber optic cable that branches from the feeder cable to serve multiple subscriber connections within a specific area or zone.
-
Feeder Cable: A high-capacity fiber optic cable that connects the central office or headend to the distribution points in the FTTH network.
-
Splitter: A passive optical device used to divide an optical signal into multiple outputs, allowing one feeder cable to serve multiple distribution points or subscribers.
-
Splice: The process of joining two fiber optic cables together using fusion splicing or mechanical splicing to ensure a continuous optical connection.
-
Splice: The process of joining two fiber optic cables together using fusion splicing or mechanical splicing to ensure a continuous optical connection.
-
Mechanical Splicing: A method of joining optical fibers using mechanical connectors without the need for fusion.
-
Optical Time-Domain Reflectometer (OTDR): A testing device used to measure the loss and detect faults in optical fibers.
-
dB (Decibel): A unit used to express the ratio of power levels in a fiber optic network, indicating signal loss or gain.
-
Bandwidth: The capacity of the FTTH network to carry data, measured in Mbps (megabits per second) or Gbps (gigabits per second).
-
Symmetrical Speed: Equal download and upload speeds provided by FTTH networks, enabling faster data transfers in both directions.
These are some of the key terminologies commonly used in the context of FTTH networks.
Understanding these terms is essential for effectively working with and managing FTTH infrastructure.
Credits: ![]()