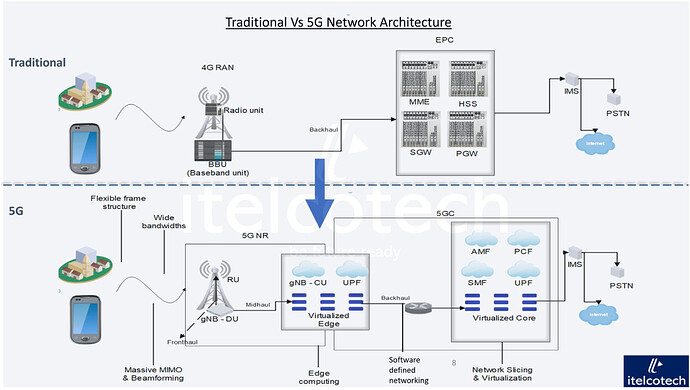
Traditional Network Architecture:
- In traditional network architectures like 4G LTE, the core network is typically centralized.
- These networks primarily rely on macrocells for coverage and capacity.
- Their functionalities are fixed, leading to higher latency.
- They offer limited support for IoT and latency-sensitive applications.
5G Network Architecture:
- 5G networks feature a distributed core network with edge computing capabilities.
- They utilize diverse cell types for improved coverage and capacity.
- 5G introduces network slicing, allowing customization for different applications.
- Designed for low latency, high throughput, and massive IoT support.
- 5G networks employ a flexible frame structure to adapt to various traffic types.
- They support wider bandwidths to accommodate higher data rates.
- Massive MIMO is used to improve spectral efficiency and coverage.
- Beamforming techniques are employed to enhance signal quality.
- Edge computing capabilities are integrated for lower latency and localized data processing.
- Virtualization technologies enable dynamic resource allocation.
- Disaggregated RAN architecture is implemented for increased flexibility and scalability.
- More intelligence incorporated by leveraging ML/AI.
There would be some other key points but above captured are the important ones.
LinkedIn: ![]()