As the world continues its rapid shift towards 5G, it’s essential to get familiar with the 5G network architecture and how different components interconnect.
Let’s break it down in a simple way.
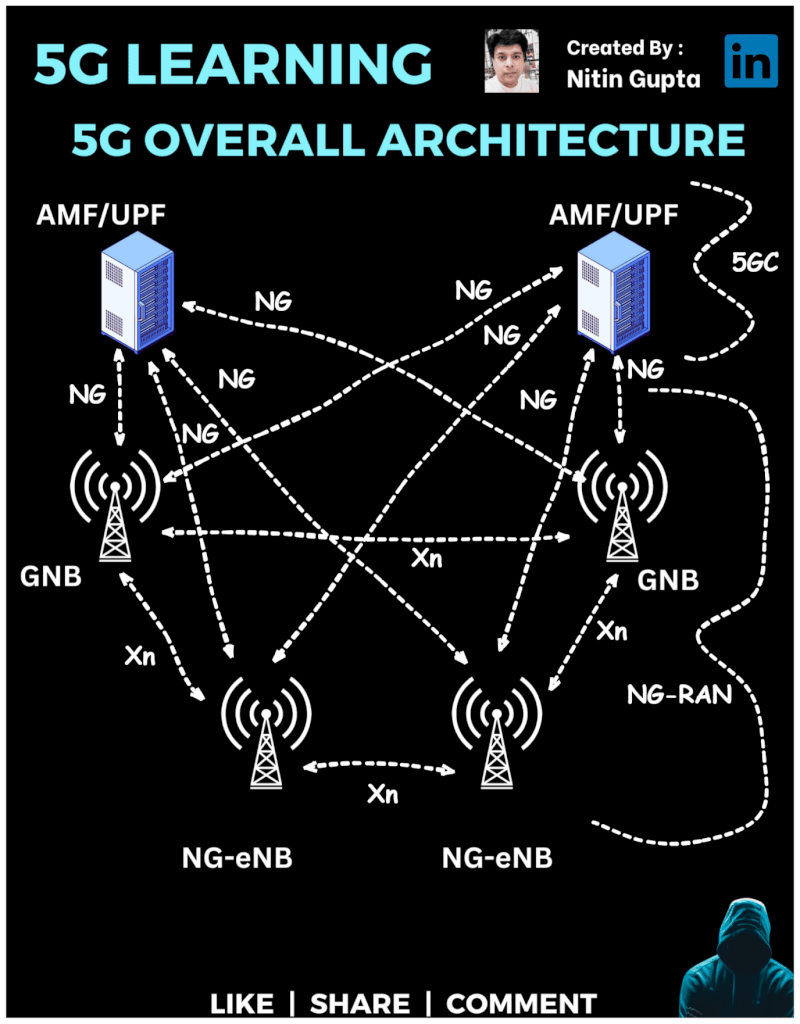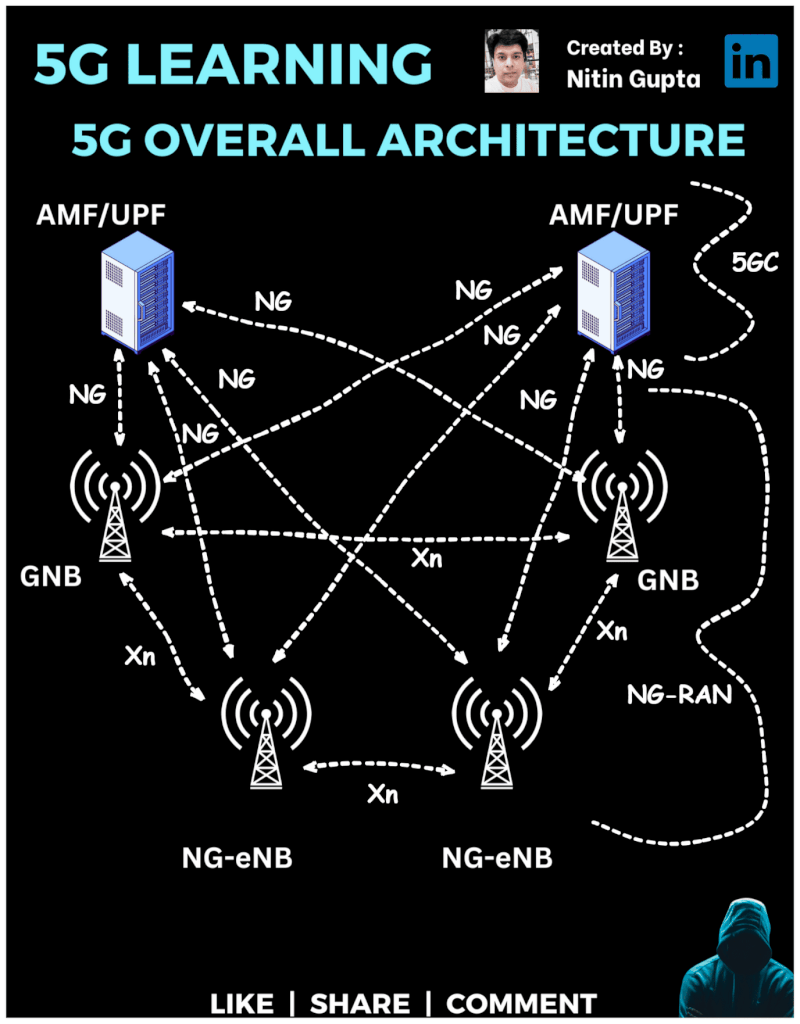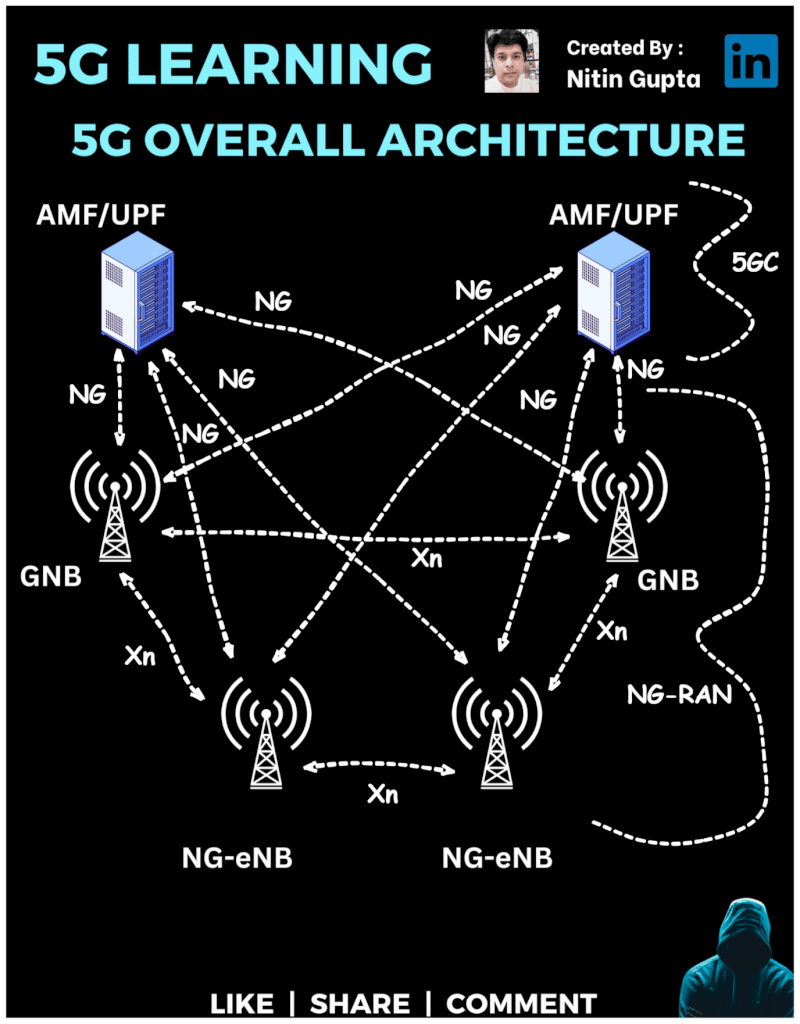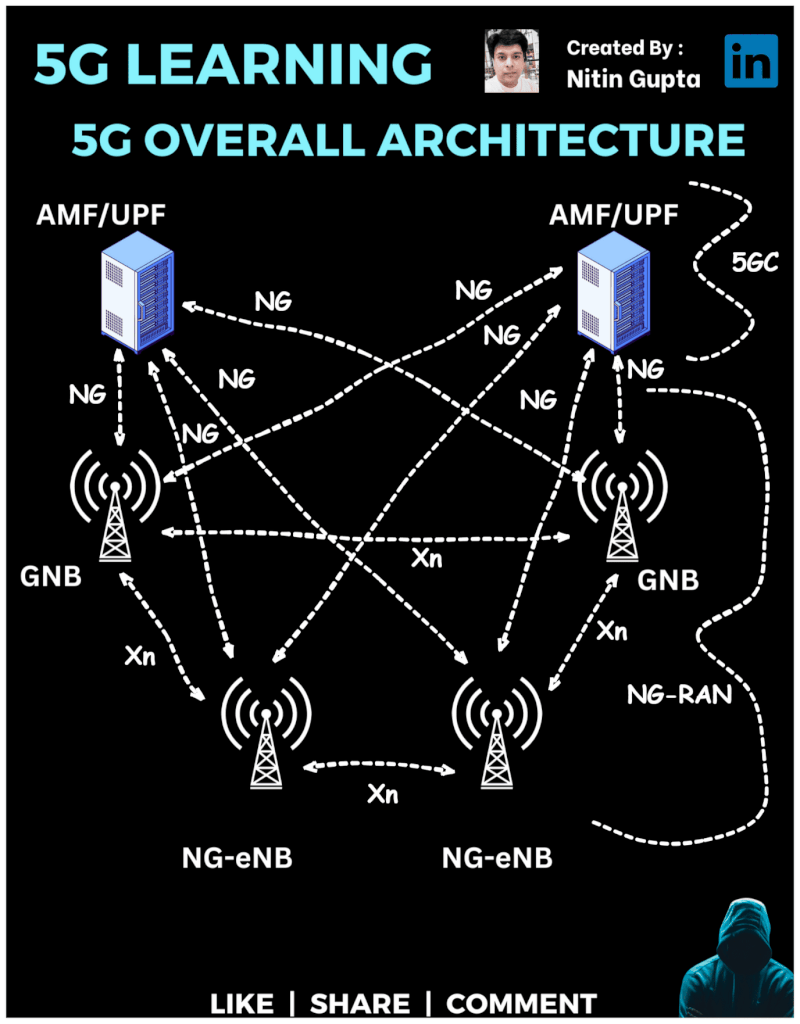
5G RAN (Radio Access Network)
In this architecture, we have:
-
gNB (Next-Generation Node B) – These are the new 5G base stations responsible for managing user devices and facilitating ultra-fast connections.
- Real-world Example: Imagine your 5G-enabled smartphone streaming 4K videos with zero buffering, thanks to the gNB handling the data flow!
-
NG-eNB (Next-Generation Evolved Node B) – These are evolved versions of 4G LTE base stations that also support 5G services, providing a seamless experience between 4G and 5G.
- Real-world Example: Picture this as your current 4G towers but now capable of supporting both 4G and 5G. They help ensure smooth transitions without sudden drops in connectivity when you move between coverage areas.
-
AMF/UPF (Access and Mobility Management Function / User Plane Function) – These are the core components of the 5G network (NG Core/5GC), ensuring fast mobility management and user data flow.
- Real-world Example: When you’re gaming online or working with cloud applications, AMF/UPF ensures a stable and lightning-fast connection by managing your device’s access and data movement.
-
Interconnections
-
NG Interface – Connects the gNB with the 5G core, ensuring efficient communication and data flow.
- Real-world Example: It’s like the high-speed highway between your phone and the main internet servers!
-
Xn Interface – Connects base stations (gNB and NG-eNB) to allow seamless communication between them.
- Real-world Example: Think of this as bridges between islands, ensuring no matter where you are, data flows smoothly across networks.
-
Why Does This Matter?
-
Smart Cities: With the rapid adoption of 5G, interconnected base stations and core components like AMF/UPF will help build smart cities by enabling technologies like IoT, autonomous driving, and high-speed connectivity.
-
Enterprise Applications: Industries will benefit from low-latency, high-speed data transfer, leading to advancements in automation, remote operations, and AI-powered services.
-
LinkedIn: ![]()