What are main reasons of Low Throughput in 4G?
There are too many Reason is possible
What’s the BW configured in transmission level?
Low mcs, Low sinr, Low rsrq , high prb usage, wrong earfcn Definition, no Carrier aggregation ör missing ca configuration, Pci , Route sequence index collision, Wrong tac planning, gateway security problem, etc.
air quality (now sinr, rsrq, etc etc), modulation level. For example, 16QAM, 64QAM, etc.
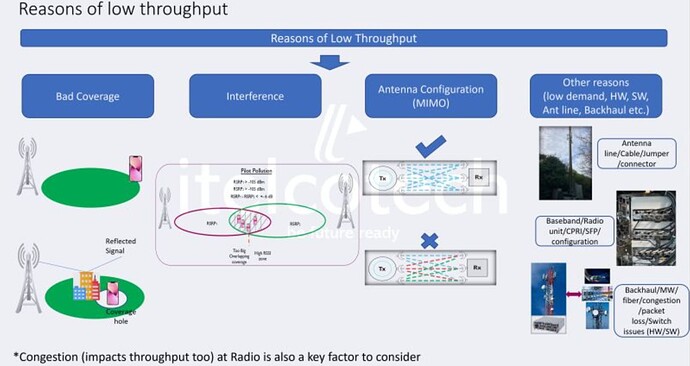
Low Throughput Issue
1 - Poor coverage (BLER)
2 - Avaibility issue
3 - Uplink Interference
4 - A poor RACH deconding SR
5 - High error on S1 link.
6 - Delay on S1 link towards MME & SGW.
7 - Accessiblity issue.
8 - Handover failure.
9 - Lack of PRBs.
10 - Problemtic UE.
11 - Downlink Interference (Bad CQI)
12 - MIMO Parameters
13 - High VSWR
14 - High radio errors or instability issue.
15 - Maximum number of RRC connections active per cell
16 - Maximum number of users per TTI supported per cell.
17 - Core network, MME/SGW, etc
18 - Transmission insability & bottleneck.
19 - Incorrect parameter setting.
20 - Badly tuned handover parameters.
21 - High traffic on Cell limit THp
Radio Analysis - Downlink
22 - CQI (Channel Quality Index) and RI (Rank Indicator) reported from UE.
23 - Transmission Mode: MIMO (tm3) vs. TxD (tm2) vs. SIMO (tm1)
24 - MCS vs. number of assigned PRBs vs. assignable bits in scheduler
25 - UE Scheduling percentage of TTIs (how often is the UE scheduled)
26 - CFI (number of OFDM symbols for PDCCH) vs. MCS vs. % scheduling
27 - HARQ
28 - RLC retransmissions
29 - Another cause of low (or lower than expected) throughput is that the UE is not being scheduled in every TTI. Packet loss can lead to (retransmissions, dropped in RBS, etc)
Radio Analysis – Uplink
30 - Uplink scheduling overview
31 - BSR (Buffer Status Report)
32 - PHR (Power Headroom Report) – is the UE at maximum power?
33 - Cell bandwidth vs. maximum allowable PRBs
34 - Link Adaptation
35 - MCS available and 16QAM
36 - PDCCH SIB scheduling colliding with UL grant
37 - HARQ (less important, because we can measure SINR)
38 - QPSK cases in UL has increased from ~30% to ~40%. If more QPSK cases then there are more UEs in poor radio conditions
Bad RSRP and RSRQ -
Issue reasons and solutions please
If Rsrp and Rsrq together goes to bad, it means there is weak coverage or weak signalization. Need to check antenna position and which site/cells should serving to there , mostly it is causes by weak coverage… Secondary issue is possible to there is handover problem among cells due to very aggresive handover parameter settings… So handover requests goes to late.
Look at parameter settings