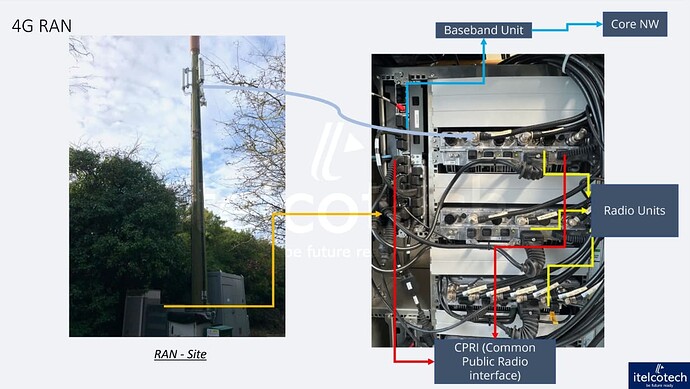
It is a crucial component of wireless communication, facilitating the connection between user devices and the core network. It consists of -
-
Baseband Unit (BBU)
It is a brain of RAN, responsible for processing the baseband signals, including
- Digital signal processing (DSP) Performing functions like Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) and Inverse FFT, modulation, and coding.
- Scheduling of resources among users
- Connects towards core network
-
Radio Unit (RU)
It is responsible for the radio frequency (RF) processing including:
- Amplification of signals
- Converts digital signals into RF signals and vice versa.
- Ensures that the transmitted signals are within the required frequency band while filtering out noise and interference.
-
CPRI Cable (Common Public Radio Interface) in 4G
It is a standard used for communication between the Baseband Unit (BBU) and the Radio Unit (RU). It is fiber optic cable, ensuring high-speed and low-latency transmission.
-
Jumpers
Jumpers are short cables used to connect radio unit and the feeder cables. It comes with low loss properties, and are RF coaxial cables capable of handling high-frequency signals.
-
Feeders
Feeders are longer coaxial cables that carry RF signals between the radio unit and the antennas. Unlike jumpers, feeders are typically deployed over longer distances with less attenuation.
-
Antennas
Antennas are transmitting and receiving RF signals between the mobile devices and the network, determining the coverage area.
Integration of RAN Components (quick recap)
- The BBU processes and prepares the digital signals for transmission.
- The signals are sent via CPRI cables to the RU.
- The RU converts the digital signals into RF signals and amplifies them.
- The RF signals travel through jumpers and feeders to the antennas.
- The antennas broadcast the signals to the surrounding area
Same applies from user device to network.
With the advancement of mobile networks, these components are continually evolving with disaggregation to meet the demand for faster speeds, lower latency.
LinkedIn: 
1 Like
A radio access network (RAN) is a major component of a wireless telecommunications system that connects individual devices to other parts of a network through a radio link.
- What components make up a RAN?
A RAN is made up of three essential elements:
-
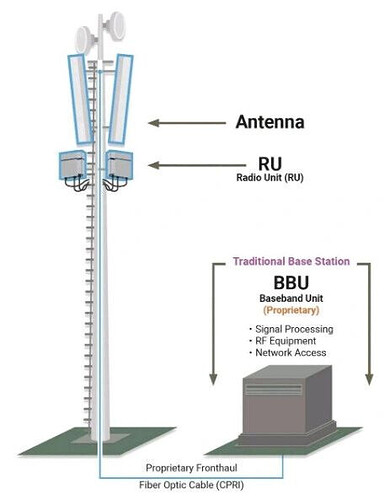
Antenna
- It interfaces with cell phone wirelessly and transmits/receivers RF signals
- It decides that shape of the coverage.
-
RRU (Remote Radio Unit)
- Interface with antenna in one side and with BBU in the anther side
- Convenes the RF signal into data signal and the vice versa
- It does filtering and amplification of the RF signal
- It decides the coverage of the power.
-
Baseband units (BBU)
Provide a set of signal processing functions that make wireless communication possible. Traditional baseband uses custom electronics combined with multiple lines of code to enable wireless communication, typically using the licensed radio spectrum.
-
Open RAN is the hot topic in the access network world now adays . It involves developing interoperable open hardware, software and interfaces for cellular wireless networks that use white box servers and other standard equipment, rather than the custom-made hardware typically used in base stations.
-
C-RAN stands for Centralized RAN which separates the radio elements in a base station into remote radio heads (RRHs). These can be used atop the cell towers for the most efficient radio coverage. RRHs must be connected to centralized baseband controllers via fiber or microwave radio links. Most baseband processing uses standard white box servers.
-
V-RAN a virtual radio access network is a type of RAN with its networking functions separated from the hardware it runs on. The control and data planes of the vRAN are also separated as part of the virtualization, this type of RAN is heavily associated with 5G networks because the networks need virtualization to support the use cases and performance requirements of 5G.
-
Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) RAN, or GRAN, was developed for 2G.
-
GSM EDGE RAN, or GERAN is similar to GRAN, but it specifies the inclusion of Enhanced Data GSM Environment packet radio services.
-
Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) Terrestrial RAN, or UTRAN, came about with 3G.
-
Evolved Universal Terrestrial RAN, or E-UTRAN, is part of LTE.
-
5G NR (New Radio) is a radio access technology relies on a fully coordinated, multi-layer network with low-band, mid-band and high-band to provide wireless connectivity to devices and deliver the best network performance.
LinkedIn: 
1 Like
![]()