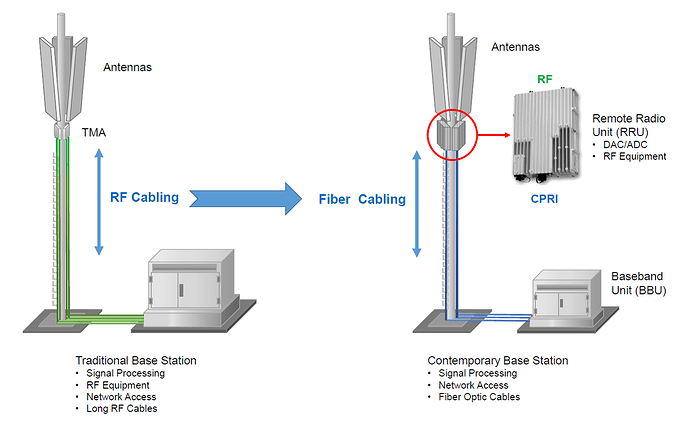
Refreshing some basic concepts.
-
BBU (Baseband Unit): manages the whole base station, including operating maintenance as will as signal processing.
-
RRU (Remote Radio Unit): interface with Antenna in one side and with BBU in the another side.
- Converts the RF signal into data signal and the vice versa.
- Filtering and amplification of RF signal.
- Decides the coverage of the power capability.
-
Antenna: interfaces with cell phone wirelessly and transmits/receivers RF signals
- Decides that shape of the coverage