Before exploring the details of fallback triggering methods and outlining the key distinctions among them, let’s address the question: Why is fallback necessary?
Fallback becomes essential when VoNR is not viable for various reasons. In such scenarios, a transition to LTE is initiated to establish voice services in VoLTE for the following situations:
- The UE lacks VoNR capability.
- The network lacks VoNR capability.
- Both the UE and the network lack VoNR capability.
- In areas with poor VoNR coverage, EPS Fallback guarantees a more dependable voice service by transitioning to LTE.
So, what are the fallback triggering methods?
3GPP outlines two mechanisms to support IMS Voice services as follows:
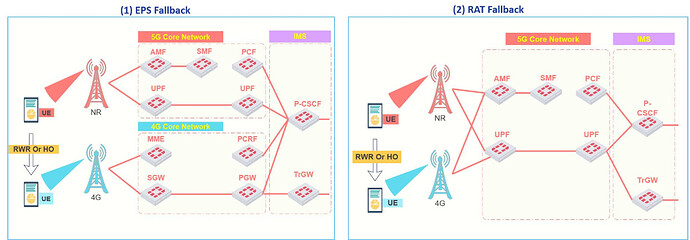
(1) EPS Fallback: In simpler terms, EPS stands for Evolved Packet System, the core network in 4G. EPS Fallback in 5G means the device switches from the 5G core to the 4G core.
- The fallback procedure moves the UE onto a 4G Core Network using EUTRA. The 4G Core Network also has connectivity to the IMS so the voice call setup can then be completed.
- PS Fallback avoids the 5G system having to support a QoS Flow with 5QI = 1, i.e. the 5G system can focus upon providing non-real time data services.
- In addition, the EUTRA Radio Access Network is likely to have wider coverage than the NR Radio Access Network (at least during early deployment) so it`s preferred at the initial stage of 5G Standalone network to use setup IMS Voice calls on the 4G Network.
(2) RAT Fallback: In simpler terms, in this triggering method, both 4G and 5G are connected to the 5G Core network. RAT Fallback, in this case, means that the user will shift from 5G RAN to 4G RAN under the same 5G Core. That’s why it’s called Radio Access Technology (RAT) Fallback.
- The fallback changes the Radio Access Network from NR to EUTRA while maintaining connectivity to the 5G Core Network. RAT Fallback avoids the NR Base Station having to support QoS Flows with 5QI = I. In addition, EUTRA Base Stations may provide better coverage than NR Base Stations -
typically due to lower operating bands and larger site
numbers during early NR deployment - The IMS voice call setup procedure then continues on EUTRA in combination with the 5G Core Network. In this case, it is not possible to trigger an SRVCC towards 2G nor 3G when the system is based upon the release 15 version of the specifications.
![]() Notes:
Notes:
- An SRVCC from 5G towards 3G is planned for the release 16 version of the specifications.
- The signaling flow associated with RAT Fallback is similar to the signaling flow associated with EPS Fallback.
LinkedIn: ![]()